Highlight the gender pay gap and other inequalities in the labor market in Mauritius. This is the objective behind the UN Women study, entitled “Why women earn less – Gender pay gap and labor-market inequalities in Mauritius” and published recently.
The context
Since gaining independence in 1968, the local economy has grown significantly. Despite these advances, achieving equality between men and women remains an ongoing challenge. The gender pay gap remains a pervasive feature of the labor market in Mauritius.
World of work: these observed inequalities
55.2% The employment rate in Mauritius is 55.2% for people aged 15 to 64 years. The employment rate of women is lower (48.6%) than that of men (78%).
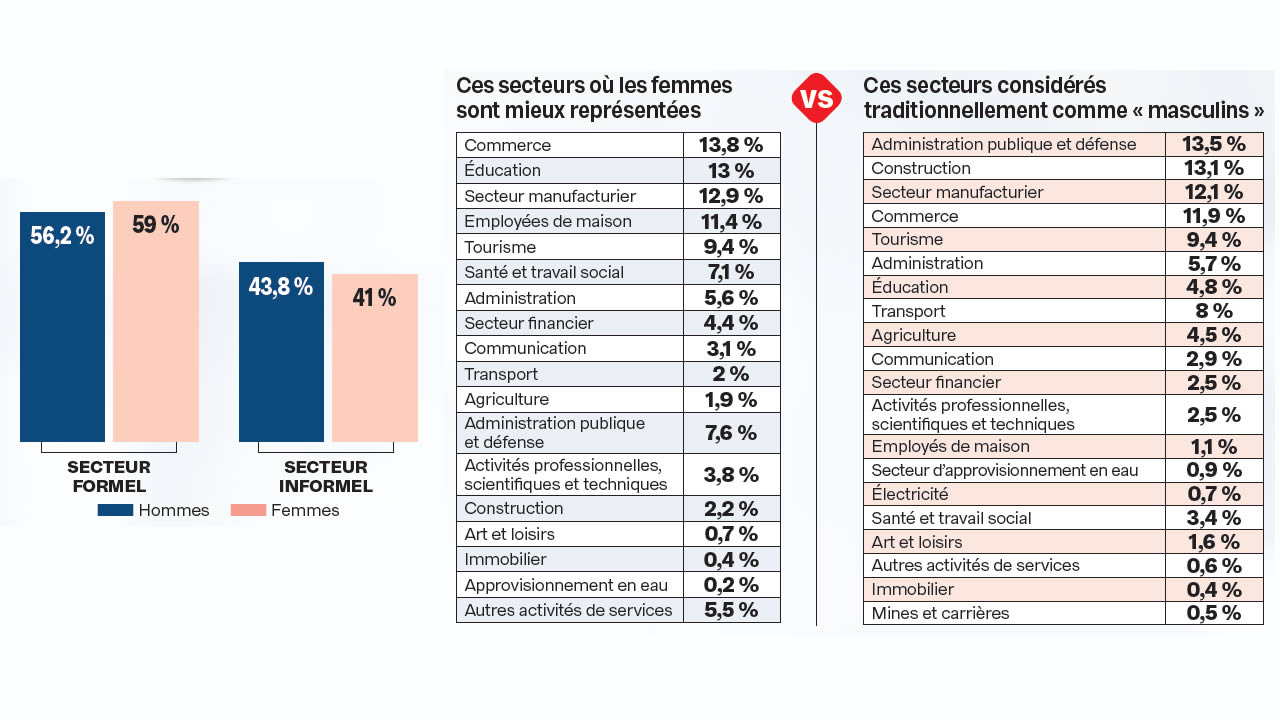
More women occupy elementary professions
| Occupations | Men | Women |
|---|---|---|
| Managers | 3.9% | 2.6% |
| Professionals | 10% | 16.2% |
| Technicians and intermediate professions | 11.5% | 12.5% |
| Office workers | 7.4% | 15.6% |
| Service staff and sales | 19.5% | 21.5% |
| Skilled workers in agriculture, forestry and fishing | 2.9% | 0.6% |
| Craftsmen | 19.8% | 3.7% |
| Machine operators and assemblers | 9.7% | 4.1% |
| Elementary professions | 15.3% | 23.3% |
Remuneration: these gaps recorded between men and women
11.3%
The gross pay gap between men and women in Mauritius is 11.3% per hour and 27.2% at the monthly level. The monthly gap is larger than the hourly gap because women work fewer hours than men. This can be attributed to different factors, including women's disproportionate unpaid care responsibilities, discriminatory labor market practices, and individual preferences.
Women are paid…
- 25.3% less than men in education.
- 17.3% less than men in commerce.
Good to know
- Women are generally paid less well in the most “feminized” sectors, that is to say those where they represent a large or majority share of employment. On the other hand, they are better paid than men in some sectors, notably mining and quarries, water supply and waste management, public administration, transport and construction (Editor's note: male-dominated sectors) .
- Women and men are distributed unevenly across sectors and occupations in the economy and this horizontal segregation is a significant factor in the gender pay gap. The overall value of occupational segregation is 0.26, which shows that about 26% of women and men would have to change occupations for the occupational distribution of women and men to become equal.
UN Women's findings and recommendations
- “Strikingly, there is a 29.4 percentage point employment gap between women and men, with women facing lower employment rates, particularly those with lower levels of employment. less educated and who belong to the oldest age group. »
- “Closing the gender pay gap and tackling other inequalities in the labor market is important to improve the socio-economic situation of women and achieve social justice…”
- “The gender pay gap and other inequalities in the labor market are complex issues influenced by various factors, such as occupational segregation, differences in education and caring responsibilities, discrimination and societal norms. »
- “Addressing these issues therefore requires a comprehensive approach involving multiple stakeholders, including governments, employers, civil society organizations and individuals. In conclusion, achieving equal pay between women and men and tackling inequalities in the labor market requires a multidimensional approach involving diverse stakeholders across the economy. »
